When is GST LUT Filing Required?
- Year-end financial reporting
- Bank funding or loan requirements
- Internal control and management review
- Periodic verification for large inventory-based businesses
Get Quote Here
OVERVIEW
Under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) law, exporters of goods or services can supply without payment of Integrated GST (IGST) by furnishing a Letter of Undertaking (LUT) in Form GST RFD-11. Filing LUT correctly and on time is crucial to avoid unnecessary tax payment and working capital blockage. Our firm provides end-to-end GST LUT filing services, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and timely submission on the GST portal.
WHAT IS LUT?
A Letter of Undertaking (LUT) is a declaration given by a registered taxpayer stating that exports will be made in accordance with GST laws without payment of IGST.
LUT is governed by Rule 96A of the CGST Rules, 2017 and is applicable for one financial year.
KEY BENEFITS OF GST
• Eliminates the cascading effect of taxes by allowing Input Tax Credit (ITC)
• Simplifies compliance by replacing multiple taxes with a single system
• Brings transparency through an online registration and return filing process
• Facilitates smooth inter-state trade and commerce
• Reduces overall tax burden and improves pricing efficiency
OBJECTIVES OF GST
• To create “One Nation, One Tax”
• To simplify indirect tax laws and procedures
• To widen the tax base and improve compliance
• To remove barriers to inter-state trade
• To increase revenue through better tax administration
IMPORTANCE OF GST
• Integrates India into a single national market
• Encourages formalization of businesses
• Improves transparency and accountability in taxation
• Helps reduce tax evasion
• Benefits consumers through competitive pricing and reduced hidden taxes
SCOPE OF WORK UNDER GST
• GST registration, amendment, and cancellation
• Determination of taxability and applicable GST rates
• Issuance of tax invoices and record maintenance
• Filing of monthly, quarterly, and annual GST returns
• Input Tax Credit (ITC) reconciliation and claims
• GST audit, assessment, and advisory services
TYPES OF GST
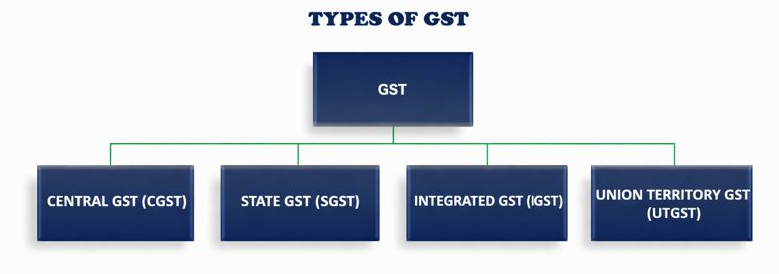
SGST (State GST) is an indirect tax levied by the state government on intrastate (within the same state) supplies of goods and services. It is levied by the state government where the product is sold or consumed. SGST ensures that the state government gets its tax revenue share from intrastate transactions. SGST has replaced earlier state-level taxes like purchase tax, luxury tax, VAT, and more.
CGST (Central GST) is imposed by the central government on intrastate (within the same state) supplies of goods and services. An equal value of CGST and SGST is levied on the same intrastate supply. If GST of 18% is levied for an interstate transaction, 9% will be the CGST rate, and 9% will be the SGST rate.
IGST (Integrated GST) stands for Integrated Goods and Services Tax. IGST is a tax imposed on all interstate supplies of goods and services between two or more states/Union Territories. It is governed by the IGST Act 2017.
Under intrastate transactions, CGST and SGST are both applied. At the same time, IGST combines these into a single tax for goods and services moving between states or union territories. The tax is then shared between the central and state governments.
UTGST (Union Territory GST) is a tax imposed on the supply of goods and services within Union territories whose governments don’t have their own legislature. It is governed as per the UTGST Act 2017. It applies to the following Union territories:
- Ladakh
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Chandigarh
- Dadra & Nagar Haveli
- Daman & Diu
- Lakshadweep
Union territories of Delhi, Jammu & Kashmir, and Puducherry have their own legislation. Hence, SGST taxation law is applicable here and not UTGST.
GST RETURN FILING
• Outward supplies (sales)
• Inward supplies (purchases)
• Input Tax Credit (ITC)
• Tax payable, paid and refund claimed
Returns are filed electronically on the GST Common Portal as per Sections 37 to 48 of the CGST Act, 2017.
TYPES OF GST RETURNS
| S. No. | Return | Purpose | Filed By | Frequency | Contains | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GSTR-1 | Outward supplies (sales) details | Regular taxpayers | Monthly / Quarterly | Invoice-wise sales, Debit/Credit notes | — |
| 2 | GSTR-2A | Purchase details (auto-generated) | Not filed by taxpayer | Auto | Supplier GSTR-1 data | ITC reconciliation |
| 3 | GSTR-2B | Static ITC statement | Not filed by taxpayer | Monthly | Eligible & ineligible ITC | For GSTR-3B |
| 4 | GSTR-3B | Summary return & tax payment | Regular taxpayers | Monthly / Quarterly | Sales, ITC claimed, Tax paid | — |
| 5 | GSTR-4 | Composition scheme return | Composition taxpayers | Annually | Turnover & tax at fixed rate | — |
| 6 | GSTR-5 | Non-resident taxable return | Non-resident taxpayers | Monthly | Taxable supplies | — |
| 7 | GSTR-6 | ISD return | ISD registered entities | Monthly | ITC distribution details | — |
| 8 | GSTR-7 | TDS under GST | TDS deductors | Monthly | TDS deducted & paid | — |
| 9 | GSTR-8 | TCS by e-commerce operator | E-commerce operators | Monthly | TCS collected | — |
| 10 | GSTR-9 | Annual return | Regular taxpayers | Annually | Annual sales, purchases & tax | — |
| 11 | GSTR-9A | Composition annual return | Composition taxpayers | Annually | Annual summary | — |
| 12 | GSTR-9C | GST audit reconciliation | Specified turnover taxpayers | As applicable | GST vs audited accounts | — |
| 13 | GSTR-10 | Final return | Cancelled GST holders | One-time | Closing GST details | — |
| 14 | GSTR-11 | UIN holder return | Embassies / UN bodies | As applicable | GST refund claims | — |
GST RETURN DUE DATES
For Regular Taxpayers
| Return | Purpose | Frequency | Due Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| GSTR-1 | Sales details | Monthly | 11th of next month |
| GSTR-1 | Sales details | Quarterly (QRMP) | 13th of month after quarter |
| GSTR-3B | Summary & tax payment | Monthly | 20th of next month |
| GSTR-3B | Summary & tax payment | Quarterly (QRMP) | 22nd / 24th (state-wise) |
| GSTR-9 | Annual return | Annually | 31st December of next FY |
| GSTR-9C | Audit reconciliation | Annually | 31st December (if applicable) |
For Composition Taxpayers
| Return | Purpose | Frequency | Due Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMP-08 | Tax payment statement | Quarterly | 18th of month after quarter |
| GSTR-4 | Annual return | Annually | 30th April of next FY |
REGULAR VS COMPOSITION SCHEME
| Basis | Regular Scheme | Composition Scheme |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Rates | Normal GST rates (0%, 5%, 18%, 40%) | Fixed low rate (1% / 5% / 6%) |
| ITC Claim | Allowed | Not allowed |
| GST on Invoice | Shown separately | Not shown |
| Interstate Sales | Allowed | Not allowed |
| Return Filing | Monthly / Quarterly | Mostly Annual |
| Compliance | High | Low |
| Suitable for | Medium & Large Businesses | Small Businesses |
| Annual Turnover Limit | No limit | Up to ₹1.5 crore (₹75 lakh for special states) |
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs)
The GST registration threshold is ₹20 lakh for service providers and ₹40 lakh for goods suppliers. For special category states, the limit is ₹10 lakh.

