When is Internal Audit Required?
- Year-end financial reporting
- Bank funding or loan requirements
- Internal control and management review
- Periodic verification for large inventory-based businesses
Get Quote Here
WHAT IS AN INTERNAL AUDIT?
Internal audit is an independent, objective assurance and consulting process that evaluates an organization’s risk management, internal controls, governance, and operational processes. Its purpose is to add value and improve efficiency, ensure compliance with laws and regulations, detect irregularities, and provide management with actionable insights for informed decision-making.
SCOPE OF INTERNAL AUDIT SERVICES
Our internal audit services cover a comprehensive range of financial, operational, and compliance areas to help organizations strengthen governance, controls, and risk management. Key areas include:
1. Financial Audit: Review of accounting records, financial statements, and adherence to applicable accounting standards.
2. Operational Audit: Assessment of business processes, efficiency, and effectiveness of operational procedures.
3. Compliance Audit: Evaluation of adherence to RBI guidelines, Companies Act, SEBI regulations, and internal policies.
4. Risk-Based Audit: Identification, assessment, and monitoring of credit, operational, market, and liquidity risks.
5. IT and Systems Audit: Review of information systems, cybersecurity, data integrity, and IT controls.
6. Fraud Detection & Prevention Identification of irregularities, weaknesses, and potential fraud risks to safeguard assets.
7. Specialized Audits Includes project audits, loan audits, stock audits, and treasury audits, especially for banks and financial institutions.
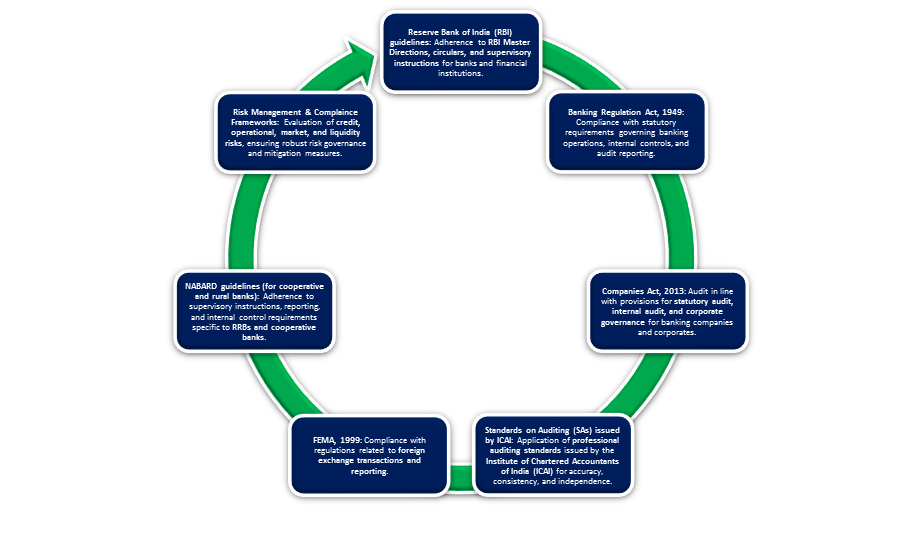
REGULATORY FRAMEWORK AND STANDARDS
Our internal and bank audit services are conducted in strict compliance with Indian laws, regulatory guidelines, and professional standards to ensure accuracy, transparency, and reliability. Key frameworks and standards include:
PURPOSE AND GOALS OF AN INTERNAL AUDIT
Internal audit is a critical function designed to evaluate, monitor, and improve an organization’s risk management, internal controls, and governance processes. The primary purpose and goals are:

Ensure Compliance

Strengthen Internal Controls

Risk Identification and Mitigation

Enhance Operational Efficiency

Detect and Prevent Fraud

Support Management Decisions

Promote Transparency and Accountability

Safeguard Assets
Ensure protection of organizational resources, cash, and investments.

Facilitate Regulatory Oversight

Build Stakeholder Confidence
IMPORTANCE OF INTERNAL AUDIT
Internal audit is a critical function that strengthens governance, enhances operational efficiency, and ensures regulatory compliance. Its importance includes:

KEY BENEFITS OF INTERNAL AUDIT
1. Enhanced Governance: Promotes accountability and transparency across the organization.
2. Stronger Internal Controls: Improves effectiveness of financial, operational, and IT control systems.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to RBI guidelines, Companies Act, SEBI regulations, and internal policies.
4. Risk Management: Identifies, assesses, and mitigates credit, operational, market, and liquidity risks.
5. Fraud Detection & Prevention: Detects irregularities and prevents errors or fraudulent activities.
6. Operational Efficiency: Optimizes processes, resource utilization, and overall productivity.
7. Strategic Decision Support: Provides actionable insights for management and board-level decision-making.
8. Asset Protection: Safeguards cash, investments, and organizational resources.
9. Transparency & Accountability: Facilitates clear reporting and responsible governance practices.
10. Stakeholder Confidence: Builds trust among investors, regulators, and employees through independent assurance.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs)
Internal audit is an independent, objective function that evaluates risk management, internal controls, governance, and compliance to improve organizational effectiveness.
Internal audit is mandatory for specified companies under the Companies Act, 2013 and for regulated entities as per RBI and SEBI guidelines.
Internal audit focuses on continuous risk assessment and process improvement, while statutory audit provides an annual opinion on financial statements.
Internal audits are conducted by qualified professionals, including Chartered Accountants, either in-house or through independent audit firms.
Internal audit covers financial controls, operations, compliance, risk management, IT systems, and fraud prevention.
The frequency depends on the organization’s risk profile, with audits conducted monthly, quarterly, or annually as per regulatory and management requirements.
Internal audit provides independent assurance, identifies risks, and offers actionable recommendations to support informed decision-making.
Yes, internal audit reports are confidential and shared only with authorized management and governance bodies.
Yes, organizations may outsource internal audit to independent professional firms to ensure objectivity and specialized expertise.

